Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
有馬 立身*; 出光 一哉*; 稲垣 八穂広*; 河村 雄行*; 舘 幸男; 四辻 健治
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 92, p.286 - 297, 2016/09
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:71.23(Nuclear Science & Technology)ウラニルイオン(UO )の拡散・吸着挙動は、放射性廃棄物処分の性能評価において重要である。溶液中のUO
)の拡散・吸着挙動は、放射性廃棄物処分の性能評価において重要である。溶液中のUO , K
, K , CO
, CO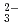 , Cl
, Cl , H
, H Oの拡散挙動が分子動力学計算によって評価された。UO
Oの拡散挙動が分子動力学計算によって評価された。UO の拡散係数が最小であり、H
の拡散係数が最小であり、H Oの自己拡散係数の26%であった。高濃度の炭酸イオンを含む溶液中では、UO
Oの自己拡散係数の26%であった。高濃度の炭酸イオンを含む溶液中では、UO CO
CO やUO
やUO (CO
(CO )
) の炭酸錯体として存在することが確認された。モンモリロナイト及びイライトと水溶液が共存する系におけるUO
の炭酸錯体として存在することが確認された。モンモリロナイト及びイライトと水溶液が共存する系におけるUO やK
やK の吸着・拡散挙動が分子動力学計算によって評価された。分配係数(Kd)は粘土鉱物の層電荷とともに増加し、UO
の吸着・拡散挙動が分子動力学計算によって評価された。分配係数(Kd)は粘土鉱物の層電荷とともに増加し、UO のKdはK
のKdはK のKdよりも小さいと評価された。さらに、2次元方向での拡散係数は、吸着層では比較的小さく、高い層電荷をもつイライトでは極めて小さな値を示した。
のKdよりも小さいと評価された。さらに、2次元方向での拡散係数は、吸着層では比較的小さく、高い層電荷をもつイライトでは極めて小さな値を示した。
Savage, D.*; Wilson, J.*; Benbow, S.*; 笹本 広; 小田 治恵; Walker, C.*; 川間 大介*; 舘 幸男
no journal, ,
高レベル放射性廃棄物の地層処分において、緩衝材の主成分であるモンモリロナイトが長期にわたり変化(変質)しなければ、性能評価で緩衝材に期待される機能は長期にわたり維持されうる。モンモリロナイトの非膨潤鉱物への変化については、これまでに半経験的速度論モデルによる評価がなされている。一方、このような評価方法は、ニアフィールドで生じる化学反応と物質移行の連成現象をモデルにより評価する方法とはアプローチが異なる。本研究では、モンモリロナイトのイライト化への変化を例に、海洋掘削プログラム(ODP Site1174)で得られた岩石コアを対象とし、上述した2つのモデルによる評価の比較を試みた。既往の研究により、半経験的速度論モデルでは、深度の増加に伴い、徐々にイライト化が進行する傾向がモデル化されており、岩石コアで認められた天然のデータ(イライト化率)とも整合的であった。一方、化学反応と物質移行の連成モデルによる評価では、より速くイライト化が進展するような結果が得られ、この要因として、緩衝材中にモンモリロナイトと共存する非晶質シリカが石英に変化することで間隙水中のシリカ濃度が低下し、イライト化を加速させる可能性が示唆された。今後は、イライト化への変化(変質)機構に関わるモデルの見直しを図ると共に、これら2つのモデルによる評価の違いの要因について、さらに考察を深める予定である。
Wilson, J.*; Bateman, K.*; 川間 大介*; 舘 幸男
no journal, ,
Several repository concepts have been proposed for the disposal of radioactive wastes, some of which include argillaceous (clay-rich) host rocks and cementitious engineered barriers. The presence of hyperalkaline cement pore-fluid results in the destabilization of primary minerals in argillaceous rocks, leading to alteration at the interface between cement/concrete and repository host rock. This phenomenon has implications for radionuclide transport and safety assessment. A general review of key data on cement-mudrock interactions has been undertaken as part of a programme of research in Japan, with experimental, analogue, and modelling studies being considered. Although a reasonably good understanding of the key processes has been acquired, with expected features of cement-mudrock interfaces being identified, there are some areas in which a degree of uncertainty remains. These include alteration under elevated temperature conditions, the kinetics of secondary mineral growth, the extent of pore clogging, and radionuclide mobility. In addition to the recent review, work is being undertaken in Japan to further the understanding of cement-mudrock interactions, including: in situ experiments, laboratory experiments, and their simulation. This work demonstrates the progress made within the Japanese programme and suggests areas where further work may be beneficial.